How Do Fatty Acids Travel Through a Cell Membrane
However in recent years there has been a fundamental shift in understanding and it is now generally recognized that fatty acids cross the cell membrane via a protein-mediated. Fatty acids can be transported into and out of cell membrane by - Sarthaks eConnect Largest Online Education Community.
Structure And Composition Of Cell Membrane Course Hero
Membrane-associated fatty acid-binding proteins fatty acid transporters not only facilitate but also regulate cellular fatty acid uptake for instance through their inducible rapid and reversible translocation from intracellular storage pools to the cell membrane.
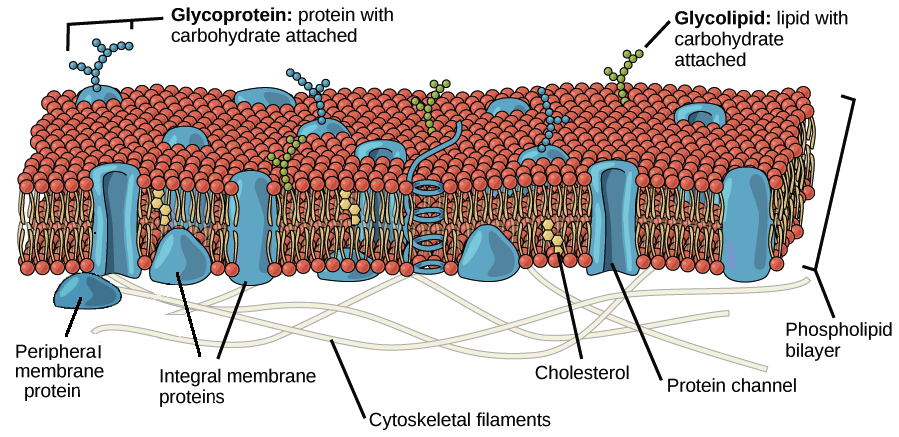
. How do fatty acids travel through a cell membrane. How do fatty acids travel through a cell membrane. Previous question Next.
Diffusion A group of single-cell organisms collected from the ocean was brought into the lab for examination. Most of the functions of a cell membrane including transport and enzymatic function are performed by. Option A is correct because fatty acids travel through a cell membrane by diffusion process.
Diffusion occurs when particles spread from areas where they are less concentrated to areas where they are more concentrated. The process of a white blood cell engulfing a bacterium is. However in recent years there has been a fundamental shift in understanding and it is now generally recognized that fatty acids cross the cell membrane via a protein-mediated mechanism.
Then how are fatty acids transported into the mitochondria. Na Sodium Diffusion does not require the cell to expend ATP. How do fatty acids travel through a cell membrane.
Transport of long-chain fatty acids across the cell membrane has long been thought to occur by passive diffusion. A number of fatty acid transporters have been identified including CD36 plasma membrane-associated fatty acid. This flip-flop mechanism has been validated in cells by intracellular pH measurements.
Transport of long-chain fatty acids across the cell membrane has long been thought to occur by passive diffusion. However in recent years there has been a fundamental shift in understanding and it is now generally recognized that fatty acids cross the cell membrane via a protein-mediated mechanism. Transport of long-chain fatty acids across the cell membrane has long been thought to occur by passive diffusion.
How do fatty acids travel through a cell membrane. The lab assistant was concerned that the water had become full of toxic waste products and so added clean water to the culture. Transport of long-chain fatty acids across the cell membrane has long been thought to occur by passive diffusion.
Therefore diffusion is considered a type of passive transport. Fatty acids can readily be transported across plasma membranes because of their lipophilicity but concentration is small in spaces devoid of FA binding proteins such as inside red blood cells. How do fatty acids travel through a cell membrane.
Lipoproteins transport triacylglycerol into tissue capillaries where endothelial lipases release the fatty acids. However in recent years there has been a fundamental shift in understanding and it is now generally recognized that fatty acids cross the cell membrane via a protein-mediated mechanism. Carrier proteins Oxygen crosses a plasma membrane by Passive transport.
Fatty acids serve as source of energy and in storage of energy. QUESTION 5 How do fatty acids travel through a cell membrane. Although transport of long-chain free fatty acids FFAs into cells is often analyzed in the same way as glucose transport we argue that the transport of the lipid-soluble amphipathic FFA molecule must be viewed differently.
How do fatty acids enter the cell. How do fatty acids travel through a cell membrane. O diffusion O active transport O carrier proteins O endocytosis.
How do fatty acids travel through a cell membrane. Fatty acids can be transported into and out of cell membrane by A Active transport B Facilitated transport C Diffusion D Osmosis. Most of a cells enzymes are.
How do fatty acids travel through a cell membrane. How do fatty acids travel through a cell membrane. A group of single-cell organisms collected from the ocean was brought into the lab for examination.
The phospholipid bilayer of plasma membrane permits small uncharged molecules like O2 and CO2 and hydrophobic m View the full answer. However in recent years there has been a fundamental shift in understanding and it is now generally recognized that fatty acids cross the cell membrane via a protein-mediated mechanism. However in recent years there has been a fundamental shift in understanding and it is now generally recognized that fatty acids cross the cell membrane via a protein-mediated mechanism.
How do fatty acids travel through a cell membrane. After the fat has been digested fatty acids are passed through the lymph system and then throughout the body via your bloodstream to be used or stored for energy cell repair and growth. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
Correct answer to the question Part A How do fatty acids travel through a cell membrane. The inner mitochondrial membrane is impermeable to fatty acids and a specialized carnitine. Transport of long-chain fatty acids across the cell membrane has long been thought to occur by passive diffusion.
Answer -C For long time it was believed thatfatty acids are travell. Transport of long-chain fatty acids across the cell membrane has long been thought to occur by passive diffusion. Carrier proteins Which substance would have the most trouble crossing a biological membrane by diffusing through the lipid bilayer.
The partitioning of FFAs into phospholipid bilayers and their interfacial ionization are particularly relevant to transport. THIS SET IS OFTEN IN FOLDERS WITH. Osmosis can be defined as.
Transport of long-chain fatty acids across the cell membrane has long been thought to occur by passive diffusion. All of the organisms died and when she looked at. View the full answer.
Newer studies have shown that fatty acids are present in membranes in the un-ionized as well as the ionized form and that the un-ionized form can cross a protein-free phospholipid bilayer quickly. Free fatty acids FFAs are then transported into cells via protein carrier mediated pathway including fatty acid translocase CD36 fatty acid transport proteins FATPs and the plasma membrane isoform of fatty acid binding protein FABPpm.

Structure Of The Plasma Membrane Article Khan Academy

The Cell Membrane Phospholipids Phosphate Head Hydrophilic Fatty Acid Tails Hydrophobic Arranged As A Bilayer Repelled By Water Attracted To Water Ppt Download
Comments
Post a Comment